In-depth analysis of the classification and industrial application of electrolytic cell
Release time:
Nov 25,2021
The form of aqueous solution electrolyzer can be divided into two types: membrane electrolyzer and non-membrane electrolyzer. membrane electrolyzers can be divided into uniform membrane (asbestos wool), ion membrane and solid electrolyte membrane (such as β-Al2O3) and other forms; membrane electrolyzers are divided into mercury electrolyzers and oxidation electrolyzers. When different electrolytes are used, the structure of the electrolyzer stack is also different.
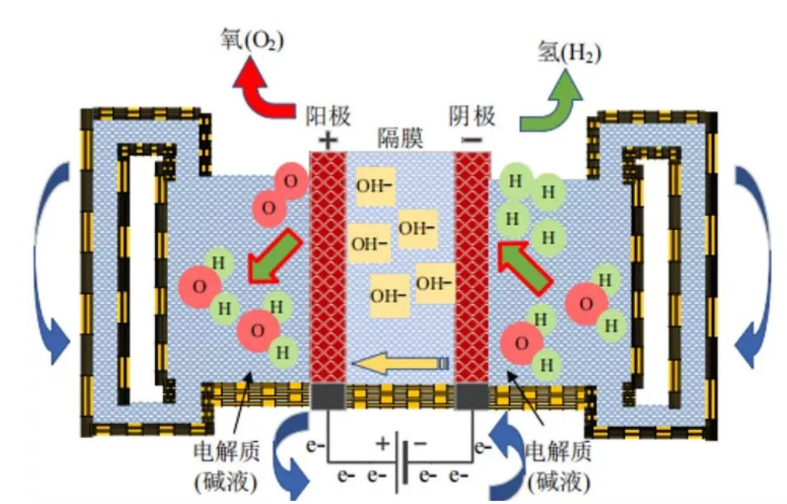
Aqueous solution electrolyzers are divided into two categories: membrane and non-membrane. General multi-use membrane electrolyzer stack. membrane-free electrolyzer stacks are used in chlorate production and mercury production of chlorine and caustic soda. The production strength of the electrolyzer stack can be increased by increasing the electrode surface area per unit volume as much as possible. Therefore, the electrodes in modern membrane electrolyzers are mostly upright. The electrolyzer stack shows different performance and characteristics due to the material, structure and installation of internal components.
It is mostly used to produce low melting point metals, which is characterized by operating at high temperatures, and should try to prevent moisture from entering and avoid hydrogen ions from reducing on the cathode. For example, when sodium metal is prepared, since the cathodic reduction potential of sodium ions is very negative, reduction is very difficult, and anhydrous molten salt or molten hydroxide containing no hydrogen ions must be used to avoid hydrogen evolution at the cathode.
For this reason, the electrolysis process is carried out at a high temperature, for example, 310 ° C. when electrolyzing molten sodium hydroxide, and about 650 ° C. when sodium chloride is contained therein as a mixed electrolyte. The high temperature of the electrolyzer stack can be achieved by changing the electrode spacing and converting the electrical energy consumed by the ohmic voltage drop into thermal energy.
Key words:
Related News




