What are the advantages of green hydrogen in the future?
Release time:
May 26,2022
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element known in the universe. With the proposal of the "dual carbon" target, aimed at achieving carbon peak and carbon neutrality, the pace of energy transition has further accelerated, and the advantages of hydrogen energy, such as high calorific value, low pollution, wide sources, and flexible conversion, are receiving unprecedented attention. In recent years, breakthrough progress has been made in the technologies of hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and application, and the hydrogen energy industry is on the eve of large-scale commercialization, expected to become the backbone of the future low-carbon energy system. As a secondary energy source, hydrogen energy can be produced not only through the reforming of fossil energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, or through biomass pyrolysis and microbial fermentation, but also through the by-product gases of industries such as coking, chlor-alkali, steel, and metallurgy, as well as through water electrolysis.
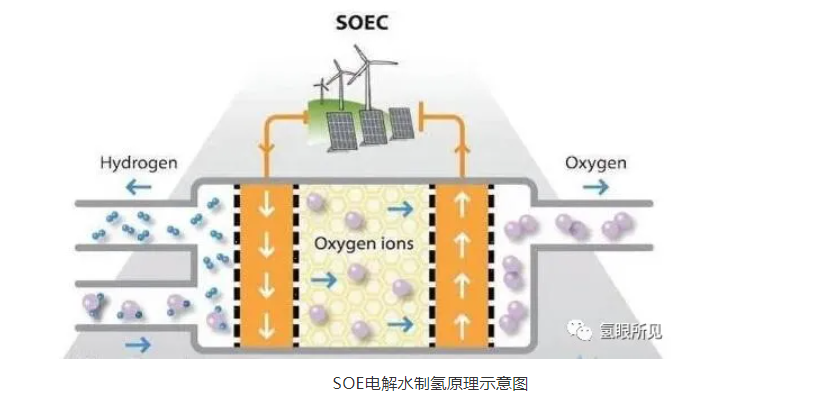
Among them, green hydrogen production using renewable energy as a raw material possesses characteristics such as environmental protection throughout the entire process, low emissions, and flexible conversion. As an alternative and supplement to renewable electricity, green hydrogen production will play a crucial role in China's path towards achieving the "dual carbon" target. Data analysis companies have suggested that hydrogen's contribution to the clean energy transition may make it a "game-changer" in the power industry. In the evolving hydrogen economy, the power industry can utilize hydrogen to replace traditional fuels.
A report titled "Hydrogen in the Power Industry - Special Discussion" pointed out that while the cost of producing hydrogen from renewable energy is currently high, the momentum built along the entire value chain is accelerating the reduction of costs associated with hydrogen production, transmission, distribution, wholesale, and terminal applications. It is now the time to continuously develop low-carbon technologies and reduce costs so that hydrogen technology can be widely applied. Hydrogen is already widely used in industries such as oil refining, ammonia, methanol, and steel. Due to progress in its application in areas such as transportation (fuel cell vehicles), construction, and power generation, hydrogen will play a crucial role in the transition to clean energy.
Key words:
Related News




